Changing the default port number of a SQL installation is one of the most basic post install steps performed. It is mainly used to make intrusion more difficult by preventing users from taking advantage of the default settings which are known in the public domain. SQL Server when install as a default instance uses port 1433. Since everyone knows this it becomes easier to target this port to try and connect to the database server.
MS SQL Server on Windows
We can change the port number by opening the configuration manager and changing the port or the TCP/IP network configurations in SQL Server Configuration manager.
Note: – this change only makes sense if connecting via TCP/IP.
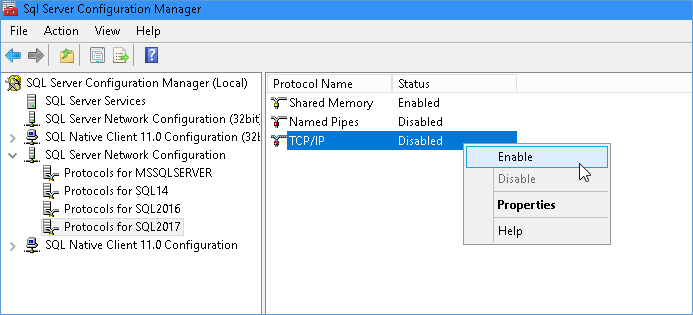
First enabled TCP/IP Connections, as you can see its disabled. Once enabled you need to restart SQL Server services in order for the changes to take effect.
After the restart double click the TCP/IP setting again and navigate to the IP Addresses tab and scroll to the IP address from which you want to accept connections. Most servers will have multiple network cards and it is a good idea to accept connections from specific NIC instead of all of them. To assign port number to all IPs in one go you ca navigate to the bottom of the tab and set TCP Port Value under IPAll section.
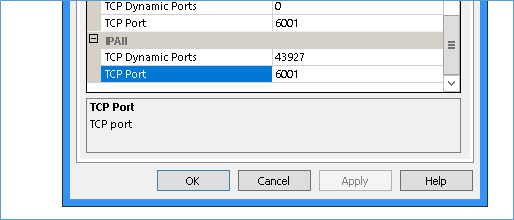
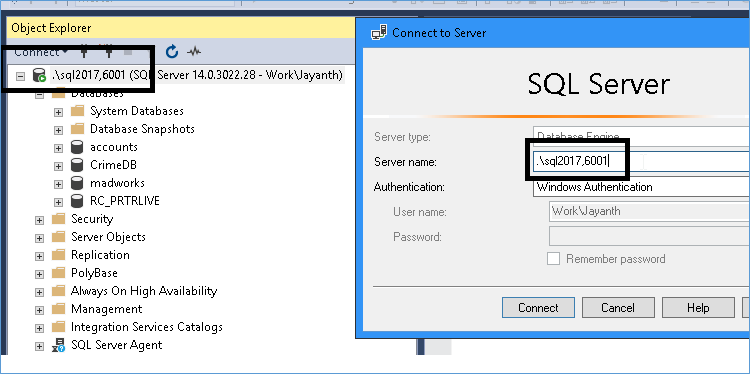
In the above screenshot I have set 6001 as the default for all NICs with the IP assigned (IPS are always static for database servers). Make sure the firewall has these ports open else they will block connections anyway. Next restart the SQL Server Service and try connecting via SSMS as shown below. Notice the comma between the server name and the port number.
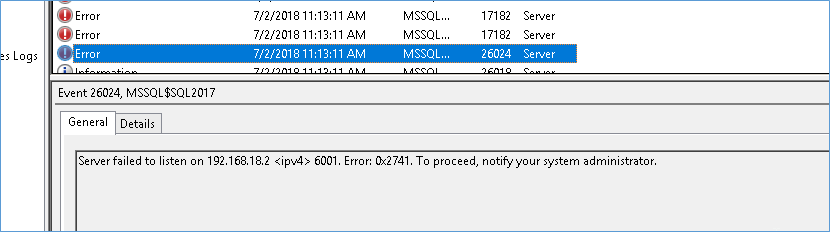
If you tell SQL server to listen to some NIC that doesn’t actually exists like maybe a Virtual IP your SQL Server instance won’t be able to restart and you will see the below error message in event log
MS SQL Server on Linux
SQL on Linux doesn’t have the same UIs as we see in windows OS so most of the work when it comes to configurations are done via terminal and mssql-conf utility
To begin you need to launch the terminal (equivalent of command prompt in windows)
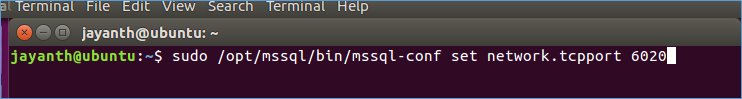
Next in the shell we need to enter the below command. Which basically says go to the location bin/mssql-conf and edit the configuration file by looking for a key called Network.tcpport and setting its value to 6020
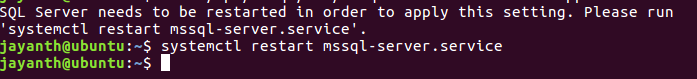
Press enter, after which you will be prompted to restart SQL Server service much like we did for windows. As you can see from the below screen the command is mentioned in the prompt you simply need to enter it as is and press Enter.
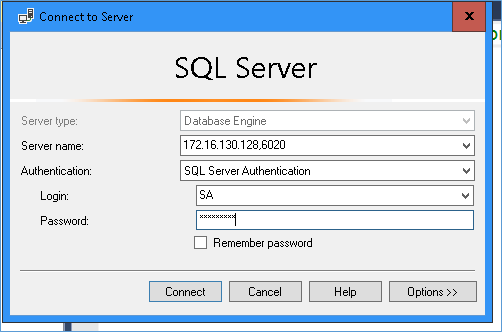
You will be prompted to enter the admin password after which the service will restart. Next open SSMS on a remote system (not available in Linux desktop, if you want to check from within Linux use SQLCMD)
Once you press connect you can check if it works properly by running @@version like the screenshot below:-
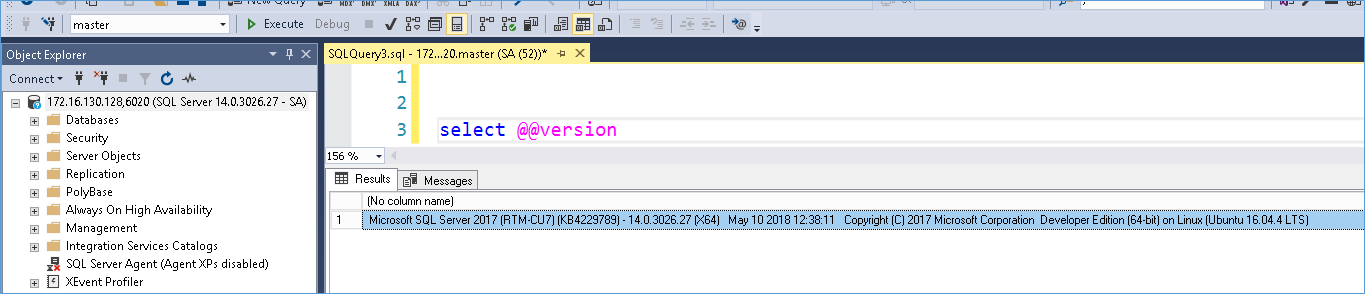
And that is all there is to it, as you can see in many ways it is much simpler to change the port number in Linux compared to Windows.
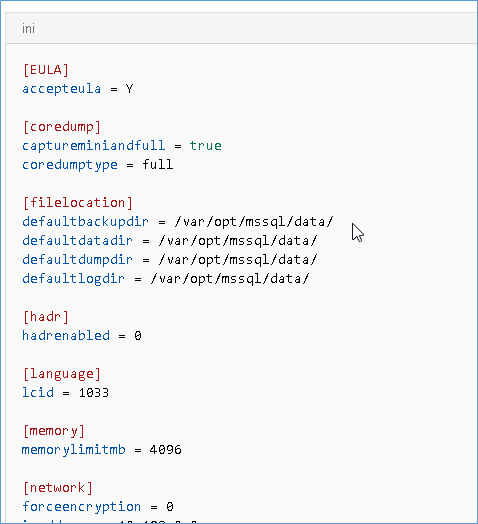
NOTE:- You can also make changes in bulk by navigating to the path /var/opt/mssql/mssql.conf and editing the file directly provided you have the required permissions, the file will look something like below
Please Consider Subscribing